티스토리 뷰
Goal
- 자바의 최상위 클래스 Object 클래스에 대해 알아본다
- Object 클래스에 정의된 다양한 메서드에 대해 알아본다
1. Object 클래스
- 모든 클래스의 최상위 클래스
- java.lang.Object 클래스로 정의되어 있으며, 컴파일시에 컴파일러가 import를 해주기 때문에, import문 없이 사용 가능하다.
- 모든 클래스는 Object 클래스에서 상속 받음
- 모든 클래스는 Object 클래스의 메서드를 사용할 수 있음.
- 모든 클래스는 Object 클래스의 일부 메서드를 재정의 하여 사용할 수 있음 (final로 선언된 요소를 제외한)
1-1 toString() 메서드
- toString() 메서드의 원형을 출력하면 참조변수에 담긴 주소값이 출력됨.
getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
- toString()을 재정의하여 객체의 정보를 String으로 바꾸어 사용할 때 유용하며 많은 클래스에서 재정의하여 사용한다.
- 자바 클래스중에는 이미 toString을 정의한 클래스가 많음 ex) String, Integer, Calendar
1-2 equals() 메서드
- 원형은 비교연산자 '=='임
- 두 객체의 동일함을 논리적으로 재정의 할 수 있음.
* 물리적으로 동일 : 주소값이 같음, 논리적으로 동일 : 실제 값이 같음.
- 물리적으로 다른 메모리에 위치한 객체라도 논리적으로 동일함을 구현하기 위해 사용
Student Lee = new Student(100, "이상원");
Student Lee2 = Lee;
Student Sang = new Student(100, "이상원");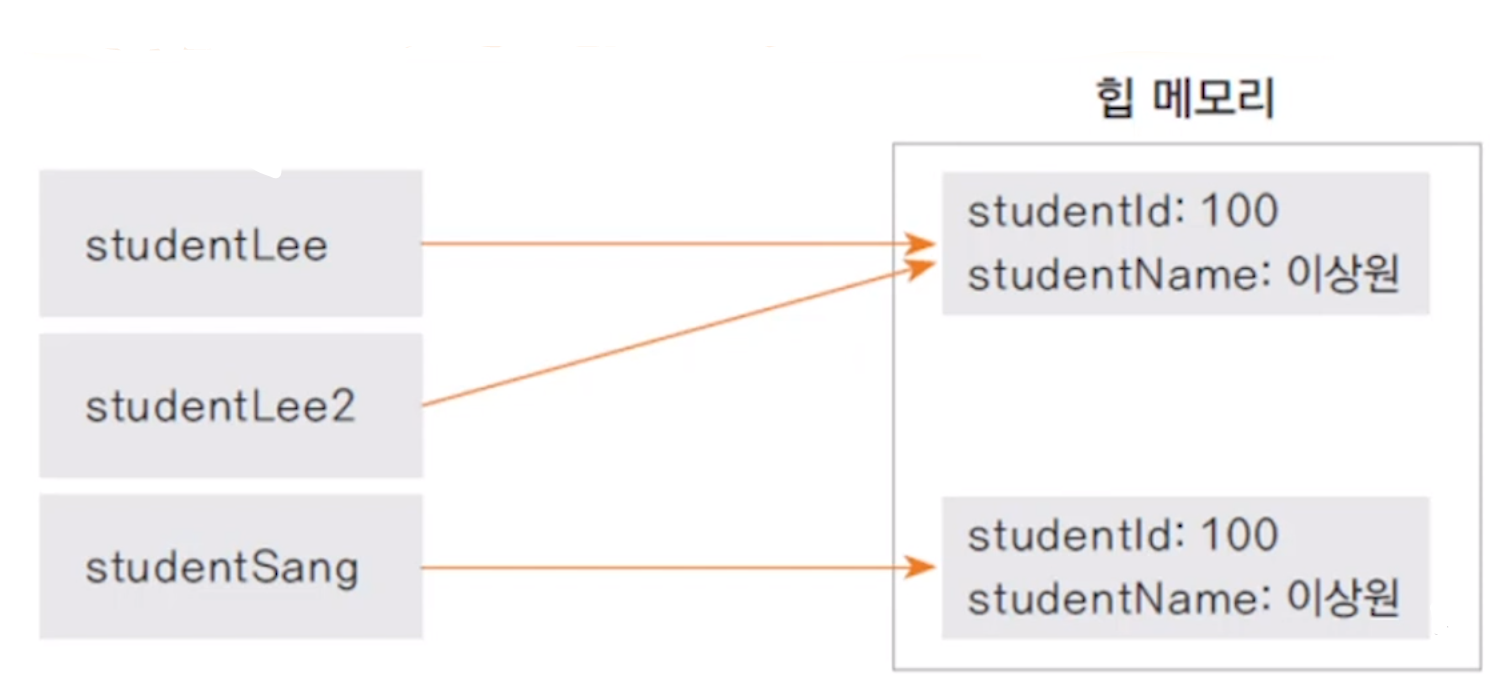
1-3 hashCode()
- hashCode() 메서드의 반환 값 : 인스턴스가 저장된 가상머신의 주소를 10진수로 반환
- 두 개의 서로 다른 메모리에 위치한 인스턴스가 동일하다는 것은?
-> 논리적으로 동일 : equals()의 반환값이 true
-> 동일한 hashCode 값을 가짐 : hashCode()의 반환 값이 동일.
- 두 객체의 equals 값이 동일하면 hashCode값도 동일하도록 여러가지 객체에서 오버라이딩을 하여 사용한다. 즉, equals()와 hashCode를 사용하여 두 개의 서로 다른 메모리에 위치한 인스턴스가 동일한 것으로 표현한다.
- hasCode를 오버라이딩할 때는, 보통 equals에서 비교한 맴버를 return값으로 넣어준다
- 두 개의 인스턴스가 서로 같은 주소값을 갖을 경우에는?
-> System.identityHashCode(obj)를 통해 주소값을 비교하여 메모리의 위치를 나타낸다.
- hashCode를 오버라이딩 하지 않으면 System.identityHashCode(obj)와 결과 값이 같아진다.
예시 코드 1) equals()를 오버라이딩하여 Student 클래스에 재정의.
class Student{
int studentNum;
String studentName;
public Student(int studentNum, String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
this.studentNum = studentNum;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Student) {
Student std = (Student)obj;
if (this.studentNum == std.studentNum) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
}예시 코드 2) equals(), == , System.identityHashCode()를 사용하여 객체간의 관계 나타내기.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student Lee = new Student(100, "이상원");
Student Lee2 = Lee;
Student Sang = new Student(100, "이상원");
System.out.println(Lee == Lee2); //true
System.out.println(Lee == Sang); //false
System.out.println(Lee.equals(Sang)); //true
System.out.println(Lee);
System.out.println(Lee2);
System.out.println(Lee.hashCode());
System.out.println(Lee2.hashCode());
System.out.println(Sang.hashCode());
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(Lee));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(Lee2));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(Sang));
}
}
1-4 clone() 메서드
- 객체의 복사본을 만듦
- 기본 틀(prototype)으로 부터 같은 속성 값을 가진 객체의 복사본을 생성할 수 있음.
- 객체지향 프로그래밍의 정보은닉에 위배되는 가능성이 있으므로 복제할 객체는 cloneable 인터페이스를 명시해야 함.
예시 코드 3) clone사용 구현
class Book implements Cloneable{
String title;
String author;
public Book(String title, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
public String toString() {
return author + "," + title;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.clone();
}
}
public class ToStringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Book book = new Book("토지", "박경리");
System.out.println(book);
String str = new String("토지");
System.out.println(str.toString());
Book book2 = (Book)book.clone();
System.out.println(book2);
}
}
1-5 finalize() 메서드
- 메서드를 main에 불러와서 사용하지 않고, 인스턴스가 힙 메모리에서 해제될 때 가비지 콜렉터가 실행한다.
- 리소스의 해제 및 소켓 close등의 역할을 수행함.
public void finalize() throws Throwable {
super.finalize();
}
* hashCode and System 참고
- 객체를 유일한 값으로 비교할 수 있는 방법은 뭐가 있을지 고민해보기
'Java > Java 올인원 패키지' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 22. 제네릭 (Java) (0) | 2020.03.19 |
|---|---|
| 21. String, Wrapper 클래스 (0) | 2020.03.19 |
| 19. 인터페이스 (Java) (0) | 2020.03.18 |
| 18. 템플릿 메서드 (Java) (0) | 2020.03.17 |
| 17. 추상 클래스, 템플릿 메서드 (Java) (0) | 2020.03.17 |
- 생활코딩리눅스
- 20201204
- 20200510
- 20200804
- chapter7
- 20200319
- 20200421
- 20200504
- 20200424
- 20200427
- 20200622
- 20200403
- chapter8
- 20200417
- 20200415
- 20200503
- 20200624
- 백준
- 20200420
- 20200425
- 20200423
- 20200428
- likelion
- 20200317
- 20200429
- 20200330
- 20200512
- 20200413
- 20200502
- 20200406
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
